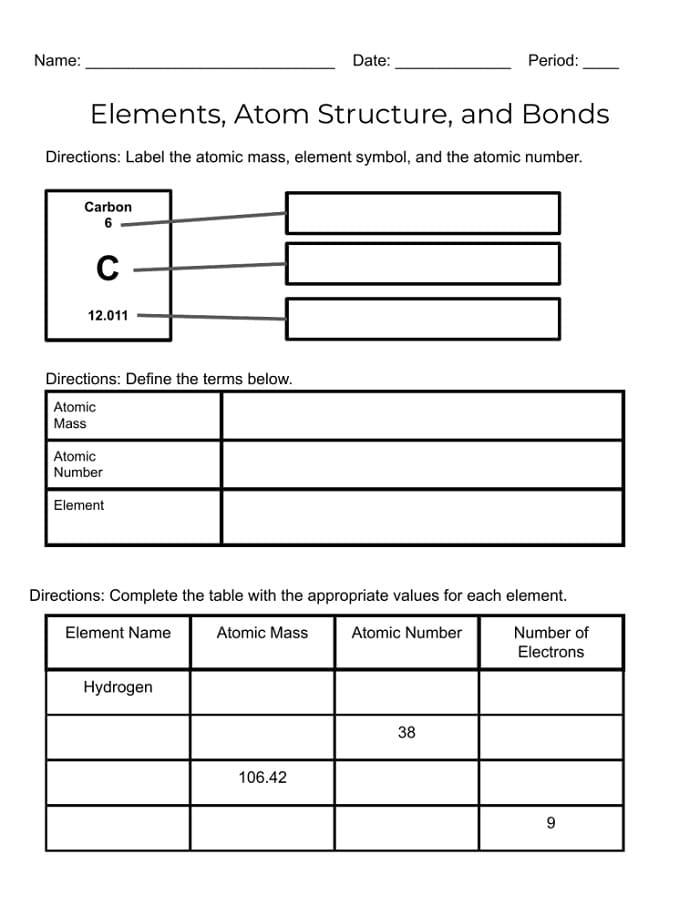
Understanding the structure of an atom is fundamental in the study of chemistry. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The arrangement of these subatomic particles within an atom determines its properties and behavior.
Atoms are composed of a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting around the nucleus in energy levels. The number of protons in the nucleus determines the element’s identity, while the number of neutrons can vary, creating different isotopes of the same element.
Electrons are arranged in shells or energy levels around the nucleus. Each shell can hold a specific number of electrons, with the innermost shell holding the least and the outermost shell holding the most. The arrangement of electrons in these shells follows a specific pattern based on the atom’s atomic number.
The structure of an atom can be represented using an atomic model, such as the Bohr model or the quantum mechanical model. These models help scientists visualize the arrangement of subatomic particles within an atom and predict its chemical behavior.
Atoms can combine to form molecules through chemical bonding, where electrons are shared or transferred between atoms. The structure of an atom plays a crucial role in determining how atoms interact with each other and form different compounds.
In conclusion, understanding the structure of an atom is essential in the study of chemistry. Worksheets that focus on the arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons within an atom can help students grasp these fundamental concepts and apply them to real-world scenarios. By completing activities and problems on the structure of an atom, students can deepen their understanding of chemistry and its applications in various fields.